Question
(a) Show that the conjectured decay of the proton, , violates conservation of baryon number and conservation of lepton number.
(b) What is the analogous decay process for the antiproton?
Final Answer
- Please see the solution video.
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 33, Problem 34 (Problems & Exercises)
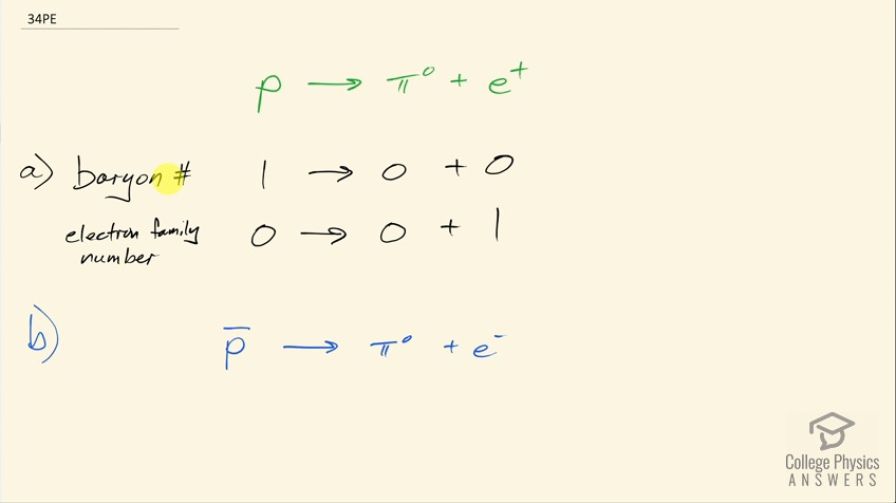
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. A proton decaying into a neutral pion and a positron violates the conservation of baryon number. When we consult table [33.2], we see the proton has a baryon number of 1 and the neutral pion has a baryon number of 0 and the electron or positron has a baryon number of 0 as well so it's 1 on the left and total of 0 on the right and so baryon number is not conserved. The electron family number is also not conserved because the proton has a 0 for the electron family number whereas the electron or positron has negative 1 and the neutral pion has 0 and this should be negative 1 there so electron family number is not conserved. This is the lepton number of concern here; there's also the tau and muon lepton family numbers but they don't matter. Okay! Part (b) asks us to write the analogous decay for the anti-proton and so we take the anti-particle for each of these and the neutral pion is strange because its anti-particle is itself and so I don't need to write a bar on top of the neutral pion and the anti-particle to the positron is the electron.