Question
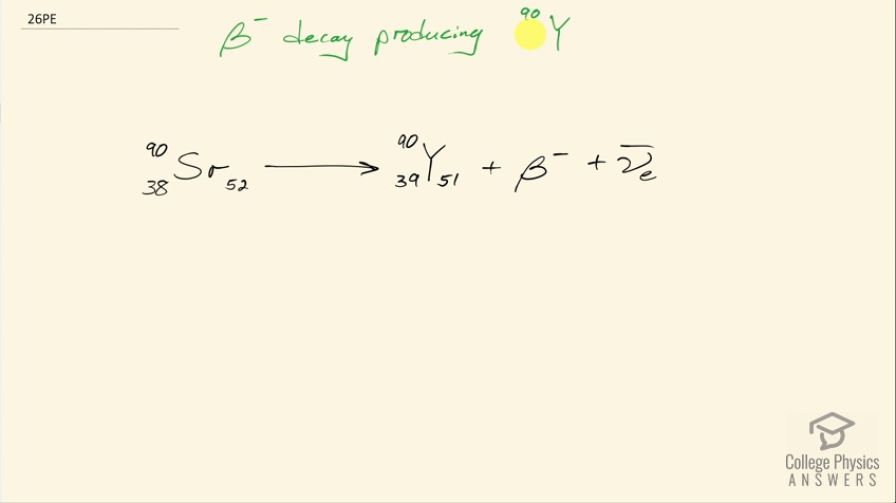
Identify the parent nuclide and write the complete decay equation in the notation: decay producing . The parent nuclide is a major waste product of reactors and has chemistry similar to calcium, so that it is concentrated in bones if ingested ( is also radioactive.)
Final Answer
Please see the solution video.
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 31, Problem 26 (Problems & Exercises)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. We are told that β decay produces yttrium-90; we should look up in this appendix at the end of the text book what the atomic number is for yttrium and it is 39 so there are 39 protons, in other words, which leaves 51 neutrons given that there are total of 90 nucleons. So we know that there is β decay so a β particle or otherwise an electron is emitted as well as an electron anti-neutrino and the question is what was the original nucleon that had this β decay occur to it. So in β decay, a neutron turns into a proton and an electron so that means there must have been an extra neutron before so 51 turns into 52 and there was once 1 less proton because now there are 39 because one of these neutrons turned into that proton so there's 1 fewer proton in this parent nuclide. So the parent nuclide has 38 protons in other words and when we look up in the appendix, the atomic number 38 corresponds to strontium. So there we go!