Question
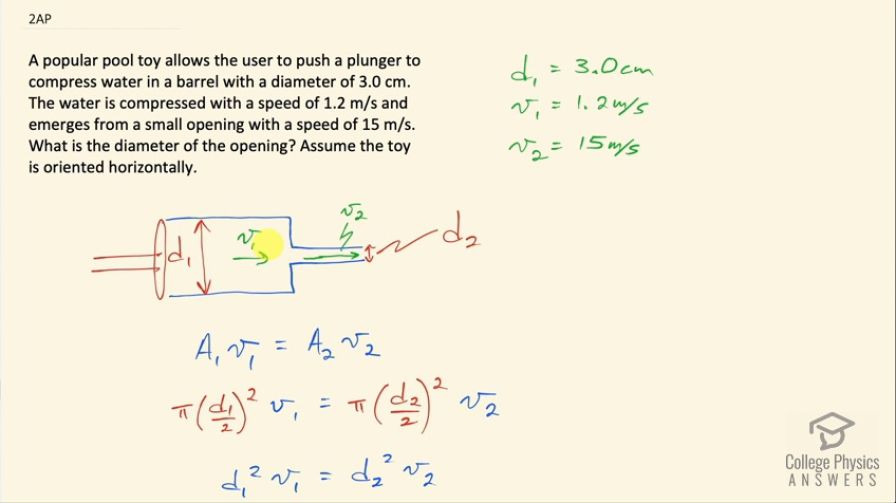
A popular pool toy allows the user to push a plunger to compress water in a barrel with a diameter of 3.0 cm. The water is compressed with a speed of 1.2 m/s and emerges from a small opening with a speed of 15 m/s. What is the diameter of the opening? Assume the toy is oriented horizontally.
Final Answer
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 12, Problem 2 (Test Prep for AP® Courses)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Calculator Screenshots
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. A pool toy has a plunger that's in a cylinder here and it's pushing some fluid with a speed v 1 through a nozzle at the end at a different speed v 2 and a different diameter d 2 and the initial diameter is d 1 and these are cylinders in which case they have cross-sectional area of a circle so π times the radius squared. Now that cross-sectional area in the first region times the speed of the fluid v 1 equals the cross-sectional area in the second region times the speed v 2— this is the equation of continuity, which says that the volume flow rate has to be the same in both regions. So we have substituting for area π times radius squared, where I have written radius as half the diameter so d 1 over 2 all squared times v 1 equals πd 2 over 2 squared times v 2 and the π and the denominator 4 cancels on both sides you can multiply both sides by 4 over π and then you get this line here: d 1 squaredv 1 equals d 2 squaredv 2 and we'll divide both sides by v 2 giving us, after we switch the sides around, d 2 squared equals d 1 squared times v 1 over v 2 and then take the square root of both sides then we get the diameter 2— the diameter of the nozzle here— equals the diameter of the big region here where the plunger is d 1 times the square root of speed 1 divided by speed 2. That's 3.0 centimeters times the square root of 1.2 meters per second divided by 15 meters per second and this is 0.85 centimeters and I left the units as centimeters and this fraction becomes dimensionless because it's meters per second divided by meters per second and so our answer is going to be in centimeters as well.
